How To Keep Your Skin Healthy: A Scientific Overview
What is healthy skin?
Your skin is far
more than just a visible surface. The skin serves as the body's first line of
defence against many physical and chemical threats, and it is frequently the
first physical layer of protection. It contains the nerve endings that tell you
whether something is hot or cold, soft or hard, sharp or dull, and it shields
you from bacteria, dirt, and other foreign objects as well as the sun's UV
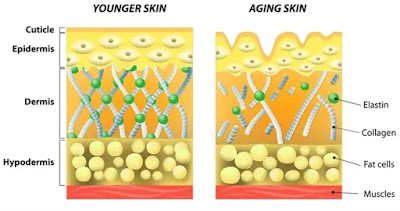
rays. The dermis and epidermis are the two main layers. While the dermis offers
structural support through its abundant network of collagen and elastin fibres,
the epidermis serves as a barrier to protect against environmental aggressors
like pathogens, chemicals, and physical injuries. The surface of healthy skin
is smooth and free of surface cracks. A healthy body is reflected in healthy
skin (1).
Healthy skin can be maintained through proper hydration, vitamin supplementation, topical cosmetics, skin microbiome, healthy non-burning sun exposure, and protection from excessive sun exposure.
In this article we can discuss some healthy supplements for resilience skin-
A balanced diet high in
fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can greatly contribute to
healthy, glowing skin, so you should increase your intake if you are
experiencing skin issues like a pressure sore or a healing surgical incision.
Important nutrients like antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals are essential for
hydrating, protecting, and preserving the general health of the skin (2, 3).
Let’s discuss one by one:
1. Green Tea: The anti-inflammatory and
antioxidant qualities of green tea make it good for skin health. It can lessen
ageing symptoms, protect against sun damage, and possibly help treat acne and
other skin disorders. One of the strongest compounds in green tea, epigallocatechin
(EGCG), reduces the amount of free radicals and ROS in the skin and inhibits
lipid peroxidation, which limits the amount of UV radiation-dependent DNA
damage (2, 3).
2. Berries: Antioxidants found in
blueberries, strawberries, and other berries guard against cell damage, lower
inflammation, and encourage skin that looks younger.
3. Leafy Vegetables: Green leafy vegetables occupy
an important place among food crops as these provide adequate amounts of
vitamins and minerals for humans. They are rich sources of vitamins like
beta-carotene, ascorbic acid, riboflavin, folic acid and minerals like calcium,
iron, phosphorous etc.
4. Citrus Fruits (Vitamin C): Vitamin C-rich foods include grapefruit, oranges, and
lemons. The synthesis of collagen, which fortifies skin and aids in wound
healing, depends on this vitamin. Studies conducted on both humans and animals
have shown that vitamin C supplementation significantly promotes wound healing
and reduces the formation of elevated scars in the skin. Skin fibroblasts need
vitamin C to produce collagen and maintain the proper ratio of collagen to
elastin in the dermis (2, 3).
5. Vitamin A: This vitamin is essential for preventing sun damage and
promoting skin cell turnover. A lack of vitamin A led to a number of skin
issues, including dryness, wrinkles, and unsightliness. Studies show that
vitamin A strengthens the skin's defences against UV-induced damage to collagen
and procollagen and protects the skin from sunburn (3, 4).
6. Vitamin E: When vitamin E and C are taken together, they protect the skin and keep the concentration of vitamin E in the dermis stable. Furthermore, by joining forces with other antioxidants, vitamin E may mitigate the consequences of previous oxidative damage (4).
7. Magnesium: The past few decades have seen a thorough
establishment of magnesium's clinical utility. A sufficient quantity of
magnesium is necessary for the production of collagen, maintenance of skin
suppleness, and reduction of wrinkles (5).
8. Selenium: For many body functions, including the prevention of
ageing, selenium is essential. It lowers oxidative stress and raises SOD and
CAT, stabilising cell membranes and protecting DNA from damage. By speeding up
ageing or increasing susceptibility to a number of illnesses, low selenium
levels may reduce human longevity. Consequently, taking enough supplements is
crucial to halting skin ageing (5).
9. Zinc: Zinc helps the body make
collagen fibres and other proteins like elastin. By boosting elastin and
collagen, zinc helps to prevent wrinkles, sagging, dryness, fine lines, and
other signs of ageing in the skin. By avoiding UV damage, scarring, dark spots,
hyperpigmentation, and texture changes, it also enhances skin tone overall (5).
Tips for maintaining good skin care:
Quit Smoking: Avoid Smoking significantly damages skin health,
impacting texture, and elasticity, and contributing to premature aging.
Apply sunscreen: Apply at
least 30 SPF of broad-spectrum sunscreen, about the size of a palm. Apply
additional sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if you perspire or
swim.
Avoid direct sun exposure: It can lead to sunburn, and premature
ageing, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Quit sugar: Avoid consuming sugary foods and drinks as well as
processed foods: Also avoid consuming too many foods having trans and saturated
fats.
Quit alcohol: Avoid alcohol consumption because it can dehydrate
the skin and alter collagen production.
Manage stress: Excessive
stress can cause acne and other skin disorders by increasing skin sensitivity.
Avoid strong soap: Strong
detergents and soaps can remove oil from the skin. Instead, use gentle
cleansers.
Disclaimer: If you are suffering from any type of skin disease, must consult a healthcare professional for better advice.
References
(1). Skin
ageing: natural weapons and strategies. Evidence‐Based Complementary and
Alternative Medicine. 2013.
(2). Recent
advances in herbal-derived products with skin anti-aging properties and cosmetic
applications. Molecules. 2022.
(3). Dietary
phytochemicals alleviate the premature skin aging: A comprehensive review.
Experimental Gerontology. 2025.
(4). Nutritional
supplements for skin health-A review of what should be chosen and why.
Medicina. 2023.
(5). Skin
minerals: key roles of inorganic elements in skin physiological functions.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022.

Comments
Post a Comment